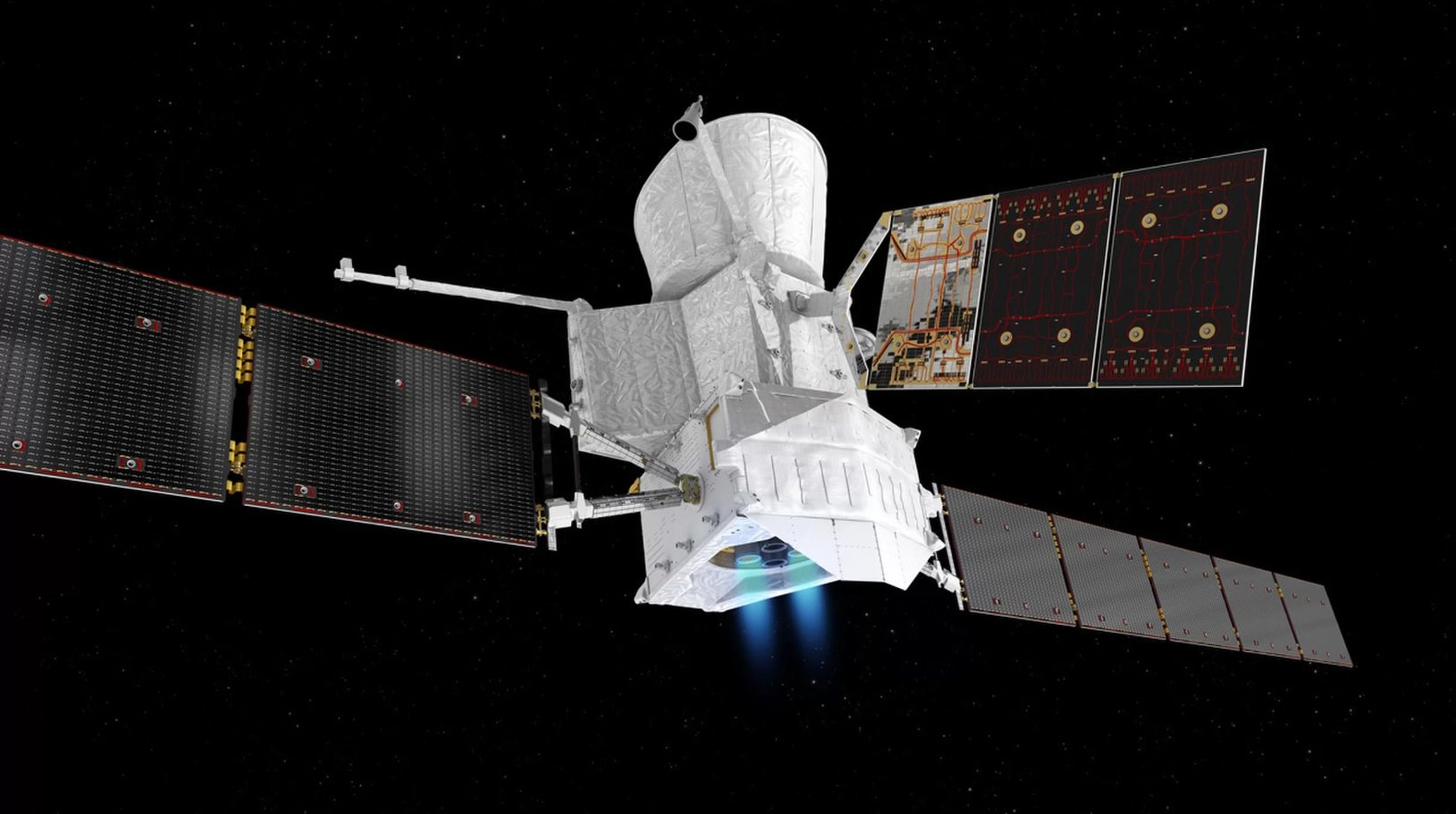
The laser guidance system will help tiny satellites to transmit data to the Earth
 Source:
Source:
The New platform laser guidance developed by the Massachusetts Institute of technology, could help small satellites to play high speed data transmission. In 1998 was launched nearly 2,000 satellites the size of a shoebox, known as . Due to its miniature form and the fact that they can be assembled from finished parts, These are much cheaper to build and run than the traditional monsters that cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
These changed principles for the establishment of satellites, because you can run them in packs for cheap monitoring of large areas of the Earth's surface. But since CubeSat equipped with more and more advanced tools, a tiny spacecraft do not have time to efficiently transfer large amounts of data to Earth due to restrictions in power and size.
theCubeSat: tiny messenger Earth
New laser-guided platform for CubeSat, is described in detail in the journal Optical Engineering, "cubitum" pass the data down, using fewer on-Board resources at much higher speeds than possible at present. Instead of having to send several images, every time "cubsat" passes through the ground station, the satellites will have the opportunity to transfer thousands of high resolution images of every span.
"to get valuable information from Earth observation, we can use a hyperspectral image that take pictures at multiple wavelengths of light and generate terabytes of data, "cubitum" it is very difficult to pass," says Kerry Kakha, associate Professor of Aeronautics and Astronautics at MIT. "But with high-speed system lasercom we will be able to send these detailed images fast enough. And I think this ability will make the whole approach CubeSat, using a multitude of satellites in orbit, more realistic, so that we can get a global and immediate coverage."
theoutside of the distribution
The Satellites usually transmit data to earth using radio waves; higher-speed lines associated with large ground-based antennas. Every major satellite in outer space communicates in high-frequency radio that allows it to quickly transfer large amounts of data. But large satellites can adapt to large radiotracer and arrays, which support high-speed transmission. "They were launched" too small and have limited access to frequency bands that support high-speed connections.
"Small satellites can not use these bands, because I need to solve a lot of regulatory issues to resolution, this usually involved the big players like large geostationary satellites," says Kakha.
Moreover, the transmitters needed for the high-speed data transmission, can use more energy than you can afford to release small satellites that support the work of the filling. For this reason, engineers have turned to lasers as an alternative form of communication for "cube-Sats", because lasers are much more compact and more efficient in energy expenditure – they compress more data in a carefully focused beams.
However, laser communication, there are also problems: since the beams are much narrower than the beams of radio waves required much more accuracy to direct the beams to a receiver on earth.
"Imagine yourself standing at the end of a long corridor and establish thick beam like from a flashlight to a target with the bullseye at the other end," says Kakha. "I can move my arm and the beam will still hit the jugular. But if I take a laser pointer, the beam can easily come up with the bullseye if I make a move. The challenge is how to keep the laser in the bullseye even if the satellite will rock".
Demonstration of optical communications and sensors, NASA uses a laser communications system for CubeSat, which inherently tilts and pushes the entire satellite to align its laser beam with a ground station. But this steering system requires time and resources, and to achieve higher data transmission speed, a more powerful laser, which can, if necessary, use a large portion of the satellite's power and generate a significant amount of heat on Board.
Kakha and her team decided to develop an accurate laser guidance, which minimise the amount of energy and time required for data transmission to earth, and would allow the use of less powerful lasers narrow, but to achieve higher transmission rates.
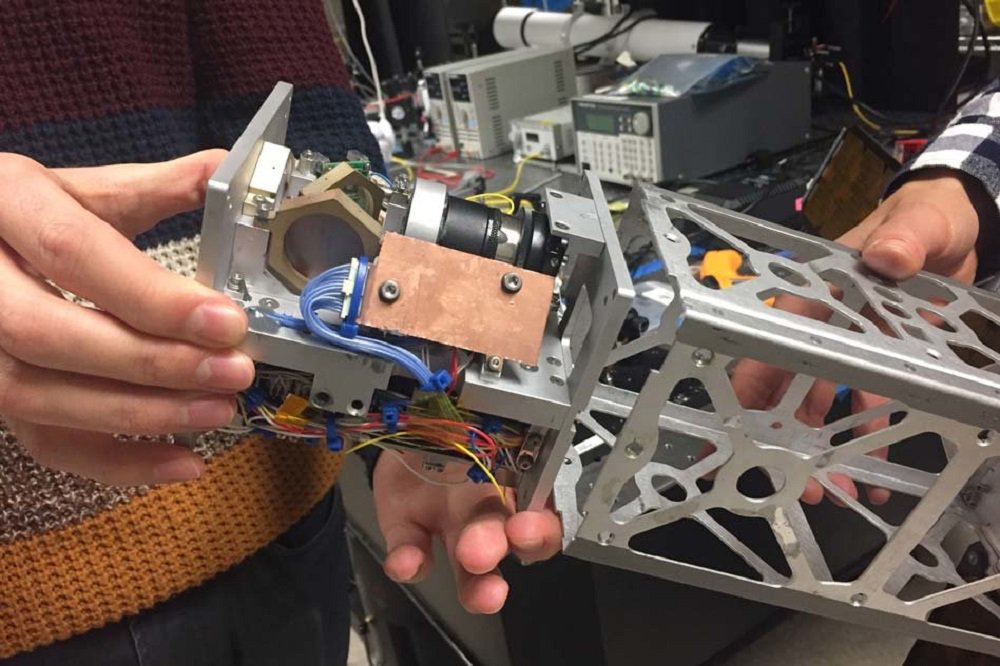
The Team has developed a platform for laser-guided, slightly larger than the "Rubik's cube", which includes small and ready driven MEMS mirror. A mirror which size is less than key on the keyboard that converts to a small laser situated at an angle so that the laser can bounce off mirrors in space and to go down to the ground receiver.
"Even if the whole satellite is slightly shifted, it can be corrected with the help of this mirror," says one of the team members. "But MEMS mirrors do not give you feedback on where indicated. For example, the mirror offset in your system, this can occur due to some vibrations during launch. How do we fix this, how to find out exactly where we specify?".
As a solution, scientists have developed a method of calibration, which determines how the laser is offset relative to the purpose of its ground station, andautomatically corrects the angle of the mirrors to accurately direct the laser to his receiver.
This method enables additional laser color, or wavelength, in an optical system. Thus, instead of just pass a bundle of data sent and the second calibration beam of a different color. Both the beam bounce off the mirror and calibration light passes through the "dichroic beam splitter", an optical element that deflects a certain wavelength of light — in this case, the complementary color is from the main beam. When the rest of the laser radiation goes to a ground station, designated beam is directed back to the on-Board camera. This camera also can take upward of a laser beam, or beacon, directly from ground stations; it will help the satellite to tune to the correct ground target.
If the lighthouse beam and the calibration beam fall exactly in the same place on the detector side of the camera, the system is aligned, and the researchers can be sure that the laser is correctly positioned for communication with the ground station. However, if the rays fall in a different part of the detector of the camera, a special algorithm directs the integrated MEMS mirror so that it tilts and the calibration laser beam is aligned with the point of the beacon ground station.
"It's like a cat-and-mouse two points coming into the camera, you need to tilt the mirror so that one dot appeared over the other."
To verify the accuracy of the method, scientists have developed a laboratory stand with a laser-pointing platform and a laser signal according to the type of beacon. The installation was to simulate a scenario in which the satellite flies at an altitude of 400 kilometers above the ground station and transmits data over a 10-minute session.
Scientists have determined the minimum required pointing accuracy in the milliradian of 0.65 — the measure of angular error is acceptable for their design. In the end, the calibration method allowed us to obtain an accuracy of 0.05 milliradians, which is much more precise than required by the mission.
"This shows that on such a tiny platform, you can install the system with low power consumption and narrow beams, and it will be 10-100 times smaller than anything that's ever been assembled like this before," says Kakha. "The only thing that would be more interesting lab results — to see it happening from orbit. That's what motivates the creation of such systems and output them in there."
Agree, it's cool? Tell us in our
Recommended
The Americans on the moon: what everyone should know?
the Upcoming cosmonautics day is my favorite holiday. It marks the triumph of the human mind: in just four thousand years Homo Sapiens went from hunter-gatherers to space explorers. 12 April 1961 Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first man in ...
Why are some galaxies spiral shaped?
you Know what surprised me the most? The fact that we perceive the surrounding world as it is. Animals, plants, the laws of physics and the cosmos are perceived by many people as something so mundane and boring that they invent fairies, ghosts, monst...
Astronomers were able to see the death of another star system
In the cosmic ocean drifts a lot of mysteries about the existence of which we are unaware. One of these was uncovered five years ago, when astronomers have discovered a lonely star at a distance of 570 light years from Earth, the brightness of which ...
Related News
NASA is developing a "tunnel-bot" with a nuclear reactor to search for life on Europa
In the course of numerous missions to Jupiter's moon Europe, it was suggested that under the thick ice layer of the moon can be uncured ocean, and it means that potentially there could be life, or at least evidence of its presence...
Astronomers have shared a real photo of the two stars, destroy each other
the Death of binary star systems can simultaneously impress with its amazing beauty and scare their destructive power. Take, as an example, a double-star system R of Aquarius, consisting of a red giant is actively discharging its ...
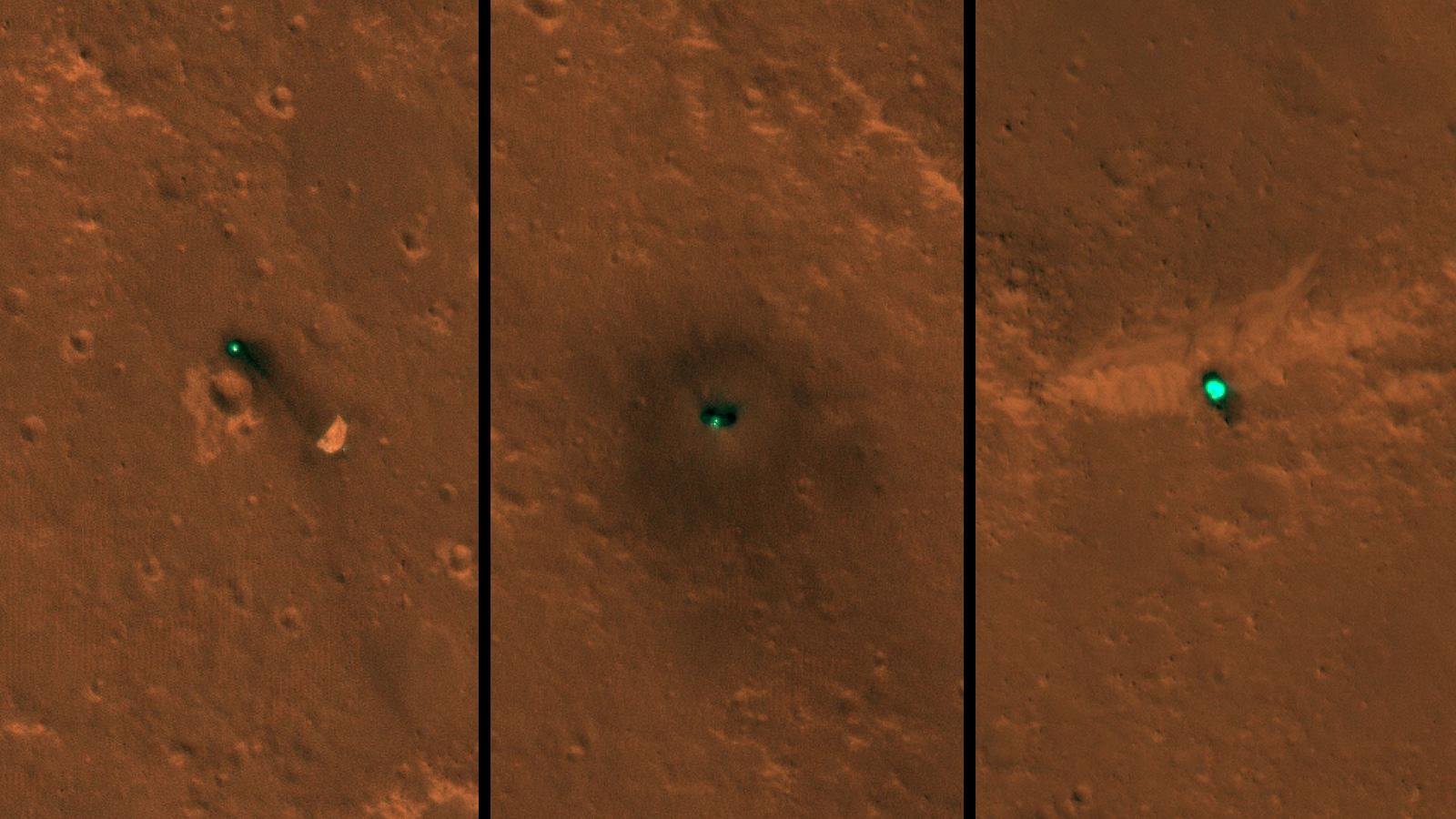
Martian machine InSight got the first pictures from space
November 26 — and worldwide, too — learned that the spacecraft of the mission InSight sat on the surface of Mars after a 130-kilometer landing on an elliptic curve. And now, a team of scientists have identified the precise locatio...
Astronomers have discovered a planet that is evaporating at a record rate
In space there is one very exotic class of exoplanets. Scientists call them "hot Neptune". They are so rare that among 3869 confirmed worlds had been discovered only a few such planets. However, their rarity may be able to explain...
10 fresh and amazing discoveries related to the milky Way galaxy
Our home galaxy is only the first frontier of space exploration. It may sound trite, but the more scientists know about it, the more amazing this system is. It has dark matter, strange signals, and many others, first discovered th...
Exoplanet is evaporating. And in the cosmic sense very quickly!
the Exoplanet almost 100 light-years from Earth disappears. And very fast by cosmic standards, are sounding the alarm astronomers. Using the space telescope "Hubble", they were able to detect GJ 3470b – exoplanet medium in size, a...
Historic flight Virgin Galactic has reminded us that "space" does not exist
just today, Virgin Galactic into space, first for myself. But once at the maximum height 82,68 kilometers, the spacecraft did not reach 17.32 kilometers to the line of Pocket — which is recognized by the world as the boundary sepa...
Six interesting experiments conducted on the ISS currently
it's been 20 years since then, as the first components of the International space station (ISS) was launched from Earth. Making a turn around the planet in 90 minutes, and at a distance of 400 kilometers above the Earth's surface,...
The Virgin Galactic spaceplane the first time made up "space height"
a Private us space company, Virgin Galactic conducted another test of a suborbital tourist spacecraft, and almost conquered the frontier of space height. The company had previously said that, as the U.S. air force to mean a height...
China successfully orbited the moon the new lunar lander and lunar Rover
Chinese space probe "Chang'e-4" with the lander and a moon Rover on Board, successfully entered the orbit of Earth's natural satellite, according to Space News. Launched by the carrier rocket "Changzheng-3B" the device has reached...
The Russian rocket for lunar exploration may cost 1.5 trillion rubles
create a super-heavy launch vehicle and use it to fly around the moon could cost the Russian budget of 1.5 trillion rubles. About it reports the edition "RIA Novosti" with reference to its sources in the space industry. As reporte...
ISS astronauts explored the hole in the "Union" and collecting samples of trim around it
Oleg Kononenko and Sergey Prokopyev during a spacewalk from the ISS opened micrometeorite protection of spacecraft "Soyuz MS-09" and found under it a hole. Samples of the sealant, which was closed on the hole and the surface aroun...
Video stream: Russian crew of the ISS went into space to check the holes in the "Union"
Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Sergey Prokopyev has walked in space aboard the International space station (ISS). This is the third spacewalk this year according to the Russian program. Before the astronauts have an importa...
Probe OSIRIS-Rex has sent a signal about presence of water on asteroid Bennu
the spacecraft OSIRIS-REx, launched in September 2016 to , beginning to bear fruit. Probe the space object recently, on 3 December, but have already discovered on the asteroid's surface water. According to researcher Amy Simon, we...
The probe "Voyager-2" reached interstellar space
Automatic spacecraft space Agency NASA "Voyager-2" has finally left the heliosphere – the region of space near the sun where the solar wind plasma is moving relative to the Sun at supersonic speed. Thus the unit became the second ...
China sent a lunar Rover on the dark side of the moon
China is the world's first launched a mission to land on the side of the moon. Start of automatic interplanetary station "Chang'e-4" on Board of the carrier rocket "Changzheng-3B" performed on December 8 at about 02:00 local time ...
Checking for care: what is unusual about this picture of the lunar Crescent?
we All know that the day sky different from the night. A truly mesmerizing night and day — at best — blind. And boring it is. Night, stars, satellites, milky Way, planets, Moon. And the day only the Moon. But wait… Astronome...
Ion engines mission BepiColombo passed the first test in space
in Addition to the validation of scientific equipment, which is one of the BepiColombo spacecraft — the joint mission of the European space Agency (EKA) and the Japanese aerospace exploration Agency (JAXA) to study mercury &...
A scientist from NASA admitted that we were able to visit the aliens. But not all so simple
recently, the Network appeared information that literally blew up the Internet. Researcher Silvano Colombano, NASA published a paper called "". The report contains some very controversial statements, but the media as one began to ...
Russia for the first time in the history of the beginning of printing bodies in space
On Board the International space station for the first time in history began , in which the bio-printer will be printed Minorcan. The results of the experiment will be released in early 2019. The experiment was carried out by labo...




































Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!