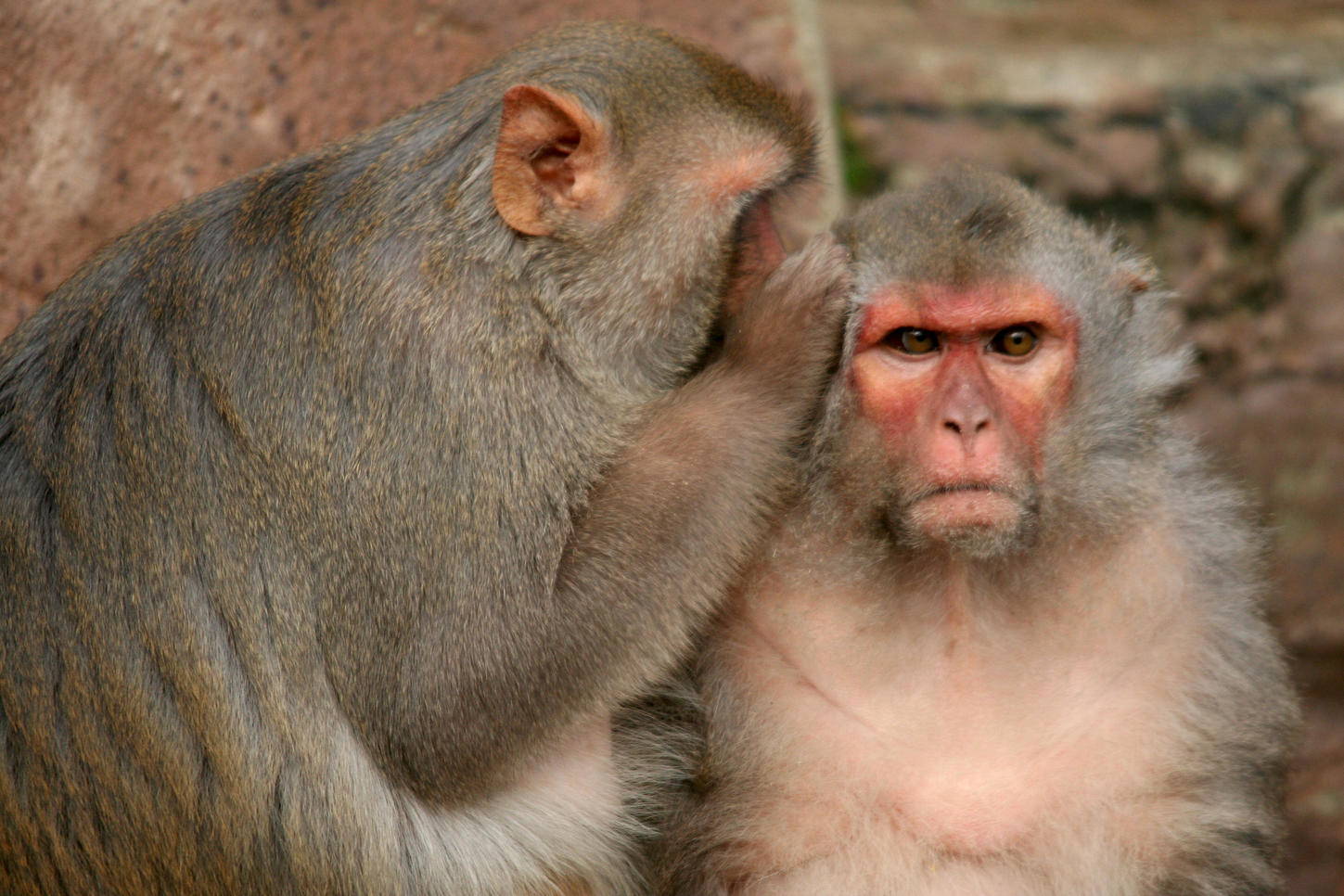
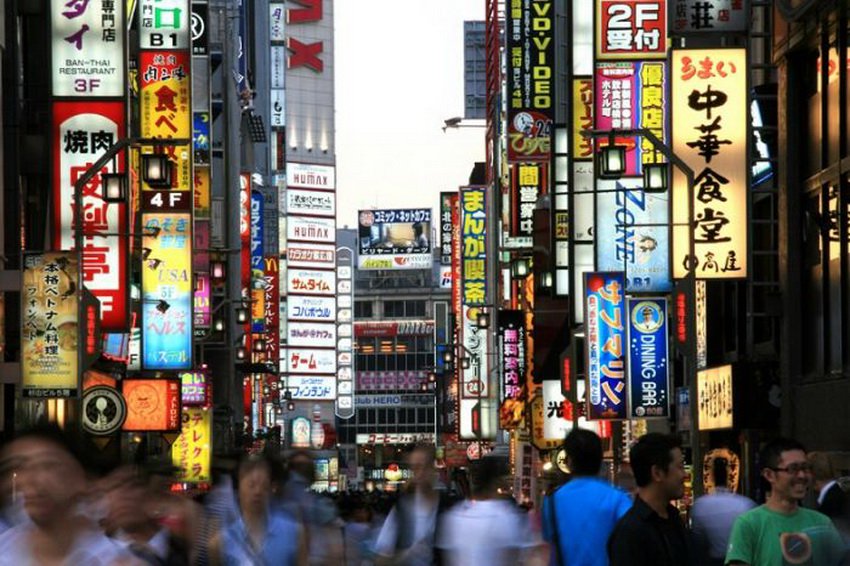
Human stem cells are returned to the monkeys the ability to grab objects
 Source:
Source:
Stem cell Therapy is very appealing in its intuitive simplicity: you clean the damaged cells trigger instead a gang of healthy, sit back and wait until the body will not should repair itself. In the case of spinal cord injury the promise of stem cells to restore mobility promises fantastic prospects. However, the human body is not a machine and not a simple system that allows you to replace parts on the fly. After transplantation stem cells are often rejected, dying in the hostile environment of the host organism even before you get a chance to recover.
Over the past thirty years neuroscientists have tried a lot of ways, I tried the cocktail with a cocktail from the special molecules that can accelerate the survival of stem cells. Although models with rodents has been a huge success, scale this therapy to work with primates and it is important for human trials to not work.
Or did not work. Last month in the journal Nature Medicine published an "important" study that detailed the recipe of transplantation of human stem cells that survived and integrated into the damaged spines of monkeys.
Nine months Later, after surgery cells dismissed hundreds of thousands of branches that formed synapses with the surviving neurons of the spinal cord of monkeys. Furthermore, spinal neurons of carriers acknowledged human cells as their own and formed new compounds that restored the animal's ability to grab objects.
the"the Growth we observed in these cells, the impressive, ten years ago I would have thought it impossible," says lead author Dr. mark Tushino from the transplantation Institute of neuroscience, University of California at San Diego. "We definitely have confidence that this treatment will work for people."
Early works
Spinal cord Injury cuts the long, thin neuronal branches — the axons — which the brain uses to communicate with the rest of the body. To restore motor function, scientists need to convince the body to repair or grow these connections.
But here's the problem. After damage to the spinal cord quickly reorganizes the extracellular matrix is a complex network of structural molecules around the injury site. Like the "bricks" on the road, these proteins effectively inhibit transplanted stem cells from stretching their long branches axenovich. Moreover, the injury also deprived of the support of growth factors and other molecules that act as a nourishing cocoon for stem cells.
To work around this double protection, the researchers formed dozens of provoking the growth of cocktails, which could give a boost transplantirovannam cells. And this strategy apparently worked.
In 2014 Tushino transformed skin cells from a healthy donor, of a person, transformed them into cells and iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cells) and implemented these artificial stem cells in a matrix containing growth factors.
After placement of graft two rats with two-week spinal injuries, human cells matured in new neurons and extended axons in the spinal cord of rats. But strangely, scientists have not seen any improvement functions partly because of the scarring at the transplantation site.
the"We're trying to do everything possible to determine the best transfer method methods of treatment involving neural stem cells in patients with spinal cord injury," said Tushino at the time.
a New hope
True to his word, Tushin experienced your Protocol transfer in monkeys that are better suited as a model for the spinal cord.
The Team crashed into a section of the spinal cord of a monkey and two weeks is sufficient time for patients stabilized — introduced human stem cells into the damaged area along with growth factors.
Didn't work. The first four monkeys introduction not even locked in place.
"If we tried to transplant on humans without prior animal testing, and would be a significant risk of failure in clinical trials", said Tushin.
Scientists quickly realized that they need to increase the number of important protein ingredient in your recipe to better to attach the graft in place. The team also found problems with the immunosuppression, timing and surgical procedure. For example, they had to tilt the surgical table during surgery, to the cerebrospinal fluid is not washed away the graft. In addition, the monkeys needed high dose of immunosuppressive drugs to the body is not attacked human cells.
With the help of some lotions grafts, each of which contained about 20 million stem cells, held in place by the remaining five monkeys.
The Results were incredible. Just two months after the transplantation, the scientists found an explosion of new neural branches. Stem cells at the injury site developed to Mature neurons, spread to 150 000 axons, which stretch in the spinal cord of a monkey.
Some of the branches were at a distance of 50 mm from the graft, of approximately the length of the two spinal fragments in humans. Along the way, they established extensive contacts with intact cells of monkeys.
What's even more cool, self axons of the apes also formed synapses with neural graft of a human, forming a reciprocal relationship. These connections are very important for free movements of the hands of people and this is one of the first clear evidence that transplanted stem cells can form such a scheme.
Nine months Later, when new neural connections helped monkeys with damage to regain movement in their limbs so that they were able to grab soft objects (e.g., oranges). In contrast, monkeys with poor grafts poorly controlled precise movement in hands and fingers — could only push orange.
The Results may seem not very impressive, but the authors say that nine months is the moment for functional recovery.
"the Grafts and the new scheme, part of which they were yet matured to the end of our observations, so the recovery can continue," said study author Dr. Ephron Rosenzweig.
Hot functional improvement was only partial, Dr. Gregoire Curtain from the Swiss Federal Institute of technology (EPFL) in Geneva, calls the study "a milestone in regenerative medicine".
"And this is not surprising, given that the functional integration of new cells and connections in the nervous system will take time and specific rehabilitation procedures," he said, adding that the study offers valuable information for potential human exploration.
Agree With him and Dr. Steve Goldman from the University of Rochester:
"It's a big jump from rodents to primates. This is a heroic study, if it comes to that".
Tushinskaya work is just beginning. First, not all stem cells are created equal, and his team is trying to determine which ones are most effective in restoring function.
On the other hand, it is also exploring additional ways to further enhance the functionality of the regenerated neurons, so that their axons can be spread through the damaged area and replace those that were lost during the injury.
"it is too early to go to the people," he warns, because further testing required. And this patience will pay off.
...Recommended
The coronavirus has mutated into 30 new strains
While coronavirus Apocalypse slowly but inevitably becomes routine, the virus SARS-CoV-2 continues to evolve. And, unfortunately, he was good at it. Writes , with reference to the South China Morning Post reports that new studies show that the virus ...
In the United States recognized that the ventilator dies 88% of patients with coronavirus
When the world is raging coronavirus that causes pneumonia and kills people, the only solution is intensive care. If this is not done, the victims will be very much. Today for severe patients there is only one solution — connected to the appara...
Can a transfusion of blood plasma to cure the coronavirus?
Typically, vaccination involves the introduction into the organism of the weakened or killed microorganisms (viruses) designed to create a strong immunity to possible future infectious diseases — that is, for selection of antibodies. But what i...
Related News
Genetic engineering will bring sight to the blind people
today it is possible to correct almost any vision from nearsightedness and farsightedness to amblyopia. But what if the vision was gone completely? Russian scientists claim that the case is not hopeless and help to the person can ...
In "SKOLKOVO" developed the first domestic device to decode the genome
the genome project required not only for research and study of genetic mutations, but in so-called personalized medicine. Is a field of science focused on the prevention of pathological processes, diagnosis and treatment based on ...
Chinese scientists have developed nanorobots that could fight cancer
Scientists from the China center of nanoscience and technology say they have managed to create and test the world's first Autonomous DNA nanorobots, capable of confronting malignant tumors. Each nanorobot is very small and cannot ...
Scientists are questioning the existing classification of diabetes mellitus
diabetes mellitus is one of the most common and almost incurable diseases today. And as you know, doctors have identified 2 types of this condition. However, according to a recent study conducted by scientists from the Swedish Lun...
Tools CRISPR mastered three new tricks
CRISPR, gene editing superhero, become a bit more powerful. Last week in Science was published three studies in which leading laboratories from around the world presented the latest additions to this technique, converting editor g...
Scientists understand the "enzyme of immortality"
About the quest for immortality or at least prolong life written not one novel, not one shot film and conducted a lot of scientific works. But the fact is that the so-called immortality enzyme was found already long enough, but to...
Google teaches the neural network to predict the death of a person
Modern medicine aims to prevent and anticipate the development of serious life-threatening diseases. However, forces and human knowledge is often not enough to predict certain complications. To help doctors in the future may come ...
Russian scientists have developed "living" bandages
Despite the fact that the skin is the body having a sufficiently high capacity to regenerate, yet with a serious injury like burns or deep wounds, it can not recover completely. Therefore, in some cases, resort to transplant skin ...
Scientists from USA have developed a synthetic analogue eyes
the New invention presented scientists from the School of engineering and applied Sciences at Harvard University — they have created an artificial eye, working on the principle of human — RIA «news» citing Th...
We often wonder why some no problems in the 9 years experience in programming (like Elon Musk, who gave the computer it was in these years) and others in this time can barely remember the multiplication table. These and many other...
Organs for transplantation will grow... in sheep
without a doubt, one of the most serious diseases are those that so strongly affect the human organs that become unable to perform its function. Then you have to resort to transplantation. However, not every transplanted organ wil...
Scientists find unusual use of the editor CRISPR genome
All people interested in science probably already heard about the editor of the genome of CRISPR. It has repeatedly used for making changes in the genetic code in a number of other similar experiments. However, as will be reported...
Microscopic somersaulting robots will be used in medicine
the Use of microscopic devices and even in medicine it becomes the last time something taken for granted. But engineers do not stop working in this direction and each year submit their new invention makes life easier for doctors a...
In Japan created the perfect remedy for the flu
Japanese pharmacists announced the creation of the drug against the flu that can kill the virus within days. It operates much faster than existing counterparts and requires only a single dose, according to the Washington Post. th...
Scientists first managed to re-create lung tissue
stem cell therapy is increasingly used in medical practice. For example, a group of Chinese researchers from Tongji University not too long ago just found a new use of a known technology, but also made a small breakthrough in medi...
Opened a way to "disable" the resistance of cancer cells to anticancer drugs
One of the main problems in the treatment of cancer is not only a very rapid proliferation of tumors but also their ability to develop resistance to different chemotherapy. This leads to the fact that the treated tumors may come b...
Doctors will use QR codes instead of drugs
Despite rapid development of pharmacology and the emergence of new types of drugs and treatment methods, the main method of delivery of tablets, capsules and pills did not change over the entire history: medications you need to dr...
Smart home not only automatiseret your life, but also help to monitor the health of
it took more than fifty years since the first time we have seen the future of smart homes, represented in the popular animated series "the Jetsons." Rumba, of course, not really like Rosie, but in modern homes the advanced technol...
Canadian scientists have created almost perpetual dental fillings
the majority of the population of our planet has those or other problems with the teeth. And almost all of us have fillings. But seals are short-lived. They are destroyed and require replacement. Recently, however, scientists have...
Scientists have discovered genes of regeneration
As you know, there are on our planet creatures that have an incredible ability to regenerate, allowing you to grow lost limbs and recover the bodies. Many scientists have long argued that virtually any body has the same possibilit...






























Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!